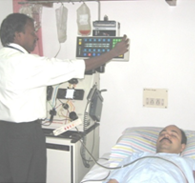
Infrastructure >> Clinical >> Apheresis
Apheresis is the process of extracting blood components with the help of an apheresis machine. Anticoagulated blood is pumped into the apheresis machine and the desired fraction is collected based on density The remaining elements are returned to the donor (or patients) by intermittent or continuous flow.
Apheresis is performed for the following components:
- Single donor platelets –The platelet apheresis product from a single person contains platelet equivalent of six to nine units of conventional platelet concentrations prepared from a single unit of whole blood.
- . Peripheral blood stem cells - Stem cells mobilized in to the peripheral blood from the bone marrow are collected for an allogeneic or autologous stem cell transplant.
- Granulocytes – Granulocytes are collected for infections which are unresponsive to antibiotics.
- Donor lymphocytes – Peripheral blood mononuclear cells collected from the original allograft donors are used for donor lymphocyte infusions (DLI) as and when indicated.
News
Publications
Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation forThalassemia Major. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2014 Dec;28(6):1187-1200. doi: 10.1016/j.hoc.2014.08.009. Mathews V, Srivastava A, Chandy M. Epub 2014 Sep 22. Review. PubMed PMID: 25459187.